How to operate a drone is a question many ask, initially seeming daunting but ultimately rewarding. This guide demystifies drone operation, from understanding its fundamental components to mastering advanced maneuvers and adhering to crucial safety regulations. We’ll explore pre-flight checks, control mechanisms, camera operation, and essential maintenance procedures, equipping you with the knowledge to confidently take to the skies.
Through detailed explanations and practical examples, you’ll gain a solid understanding of how to operate a drone safely and effectively. Whether you’re a beginner or seeking to refine your skills, this comprehensive guide will serve as your trusted companion on your drone piloting journey.
Drone Parts and Components
Understanding the individual components of your drone is crucial for safe and efficient operation. Each part plays a vital role in the drone’s functionality, and familiarity with their functions will aid in troubleshooting and maintenance.
Drone Component Breakdown
| Component | Function | Importance | Troubleshooting Tips |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Generate thrust to lift and propel the drone. | Essential for flight; damaged propellers can lead to crashes. | Inspect for cracks or damage before each flight; replace damaged propellers immediately. |
| Motors | Rotate the propellers, providing the necessary power for flight. | Provide the force for movement and stability; motor failure can cause a loss of control. | Check for unusual sounds or vibrations; ensure proper motor connections. |
| Flight Controller | The “brain” of the drone, controlling all aspects of flight, including stability and responsiveness. | Crucial for stable flight and responsiveness to pilot commands. | Recalibrate the IMU and compass if experiencing erratic flight behavior; check for firmware updates. |
| Battery | Provides power to all drone components. | Without power, the drone cannot fly; battery life determines flight time. | Check battery voltage and health before each flight; use only compatible batteries. |
| GPS | Provides location data for precise positioning and autonomous flight modes. | Essential for features like return-to-home (RTH) and waypoint navigation. | Ensure a clear view of the sky for optimal GPS signal acquisition. |
| Camera | Captures photos and videos. | Allows for aerial photography and videography. | Check the camera lens for dirt or obstructions; ensure proper camera settings. |
Drone Battery Types and Characteristics
Drone batteries are typically lithium polymer (LiPo) batteries, characterized by their high energy density and lightweight nature. Different batteries offer varying voltage, capacity (measured in milliampere-hours or mAh), and consequently, flight time. A higher mAh rating generally indicates a longer flight time. Voltage is usually standardized within a drone model, but it’s crucial to use only the manufacturer’s recommended battery.
For example, a 3S 1500mAh battery might provide 15-20 minutes of flight time, while a 4S 2200mAh battery could offer 25-30 minutes. Always refer to the manufacturer’s specifications for accurate flight time estimations.
Drone Propeller Comparison
Different propellers affect a drone’s flight performance in terms of speed, maneuverability, and efficiency. Propellers are characterized by their size (diameter and pitch), and the material they are made from. Larger propellers generally provide more thrust, while a higher pitch leads to increased speed but potentially reduced efficiency. Carbon fiber propellers are known for their strength and lightweight nature.
For instance, a drone with slow-spinning, high-pitch propellers will be faster but might consume more battery power. Conversely, a drone with fast-spinning, low-pitch propellers will be more efficient and provide better maneuverability at lower speeds. Choosing the right propeller depends on the intended use and flight style.
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist is essential for safe and successful drone operation. Neglecting these checks can lead to accidents or equipment damage. Always prioritize safety.
Pre-Flight Checklist
- Check battery level and ensure it is fully charged.
- Inspect propellers for damage or cracks.
- Visually inspect the drone for any loose parts or damage.
- Ensure all connections are secure.
- Calibrate the compass and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit).
- Acquire a strong GPS signal (indicated by the number of satellites locked).
- Perform a pre-flight system check using the drone’s app or controller.
- Check local weather conditions and airspace restrictions.
Compass and IMU Calibration
Calibrating the compass and IMU is vital for accurate flight and stability. The compass provides directional information, while the IMU measures the drone’s orientation and movement. Incorrect calibration can lead to erratic flight behavior. Most drone apps provide instructions for calibrating these components. Typically, this involves rotating the drone slowly in a figure-eight pattern.
Visual Inspection
A visual inspection is crucial to identify any potential problems before flight. Look for loose screws, damaged propellers, or any other visible damage. This simple step can prevent costly accidents.
Basic Drone Operation and Controls
Understanding the basic flight controls and modes is fundamental to safe drone operation. Start with beginner mode and gradually progress to more advanced modes as your skills improve.
Flight Modes
Most drones offer various flight modes to cater to different skill levels and flight situations. Beginner mode typically limits speed and responsiveness, providing a more stable and forgiving flight experience. Sport mode increases speed and responsiveness, suitable for more experienced pilots. Manual mode offers complete control over the drone, but requires significant skill and practice.
Drone Controls
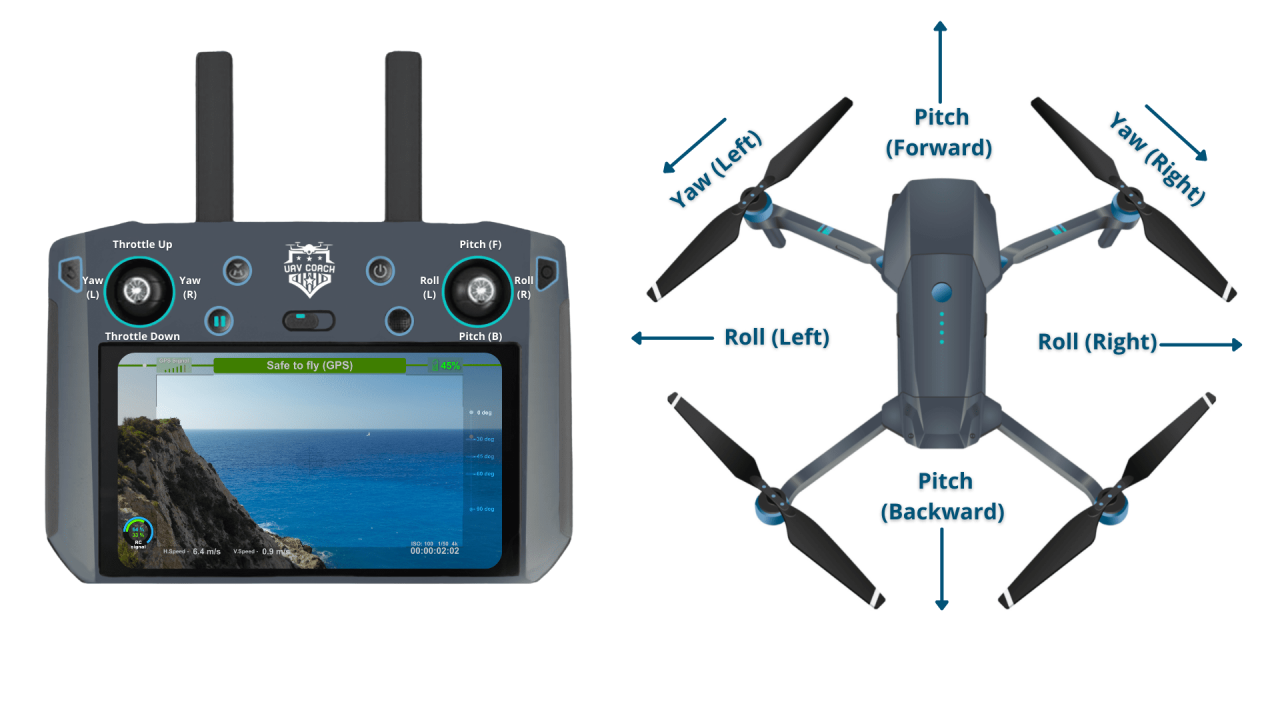

Drone controllers typically feature joysticks or thumbsticks to control altitude, direction, and speed. One joystick often controls the drone’s pitch and roll (forward/backward and left/right movement), while the other controls yaw (rotation) and throttle (altitude).
Basic Drone Maneuvers
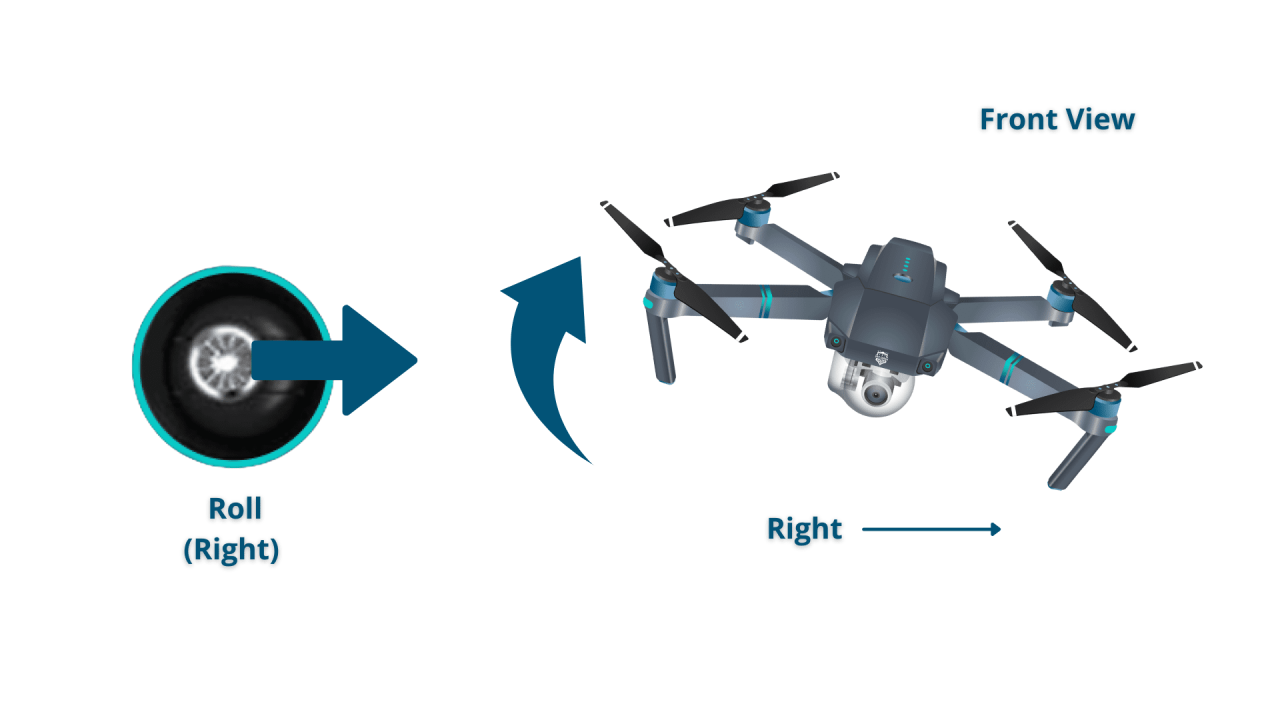
Mastering these basic maneuvers is essential before attempting more advanced techniques. Practice in a safe, open area away from obstacles.
- Taking Off: Engage the throttle slowly and smoothly to lift the drone vertically.
- Landing: Gradually reduce the throttle to lower the drone gently to the ground.
- Hovering: Maintain a stable position in the air without moving horizontally or vertically.
- Moving in Different Directions: Use the control sticks to move the drone forward, backward, left, right, and diagonally.
Advanced Drone Maneuvers and Techniques
Once comfortable with basic operation, you can explore more advanced maneuvers. These require practice and a good understanding of drone dynamics.
Complex Flight Maneuvers
Advanced maneuvers include circling, orbiting, and precise positioning. Circling involves maintaining a constant radius around a point. Orbiting uses GPS to maintain a circular path around a set point. Precise positioning uses GPS or visual sensors to maintain a specific location.
Waypoints and Autonomous Flight
Waypoints allow you to program a flight path by defining a series of GPS coordinates. The drone will autonomously follow this path, making complex maneuvers easier. Autonomous flight modes, such as follow-me or point-of-interest, further enhance the drone’s capabilities.
Example Flight Plan
- Take off and ascend to 50 feet.
- Move forward 100 feet.
- Circle a specific point for 10 seconds.
- Orbit a different point for 20 seconds.
- Return to the starting point.
- Land smoothly.
Drone Camera Operation and Photography/Videography: How To Operate A Drone
Understanding camera settings and techniques is crucial for capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos. Experimentation and practice are key to mastering this aspect of drone operation.
Successfully operating a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource to begin your journey is this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. This will help you confidently navigate the process of piloting and mastering the various functionalities of your drone, ensuring safe and enjoyable flights.
Camera Settings
Camera settings like resolution, frame rate, ISO, and shutter speed significantly impact image quality. Higher resolution produces larger files but requires more storage space. Frame rate affects the smoothness of video. ISO controls sensitivity to light, while shutter speed determines exposure time.
Tips for High-Quality Aerial Media
- Shoot during the “golden hour” (sunrise and sunset) for optimal lighting.
- Use a polarizing filter to reduce glare and enhance colors.
- Maintain a steady flight to avoid blurry images.
- Experiment with different angles and perspectives.
- Understand the relationship between aperture, shutter speed, and ISO.
Camera Features
Most drone cameras offer features such as zoom, focus, and various video recording modes. Understanding these features enhances creative control and allows for capturing diverse shots.
Drone Safety and Regulations
Adhering to local regulations and safety procedures is paramount for responsible drone operation. Ignoring these guidelines can lead to fines, accidents, and legal repercussions.
Drone Regulations and Airspace Restrictions
Familiarize yourself with local and national regulations regarding drone operation. These regulations often specify altitude limits, airspace restrictions (near airports, for example), and required registrations. Always check for updated regulations before each flight.
Safety Procedures
- Maintain visual line of sight with your drone at all times.
- Avoid flying near people, animals, or obstacles.
- Fly in appropriate weather conditions (avoid strong winds or rain).
- Be aware of surrounding airspace and other aircraft.
- Never fly under the influence of drugs or alcohol.
Emergency Procedures, How to operate a drone
- If you lose control of the drone, attempt to bring it down in a safe, open area.
- Contact local authorities if your drone causes damage or poses a hazard.
- If the drone malfunctions, land it immediately and assess the damage.
- If the drone is lost, try using the return-to-home (RTH) function.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and prompt troubleshooting are crucial for extending the lifespan of your drone. A well-maintained drone is safer and more reliable.
Regular Drone Maintenance
- Clean the drone body and propellers after each flight.
- Inspect propellers, motors, and other components for damage.
- Check battery health and charge levels.
- Lubricate moving parts as needed (refer to manufacturer’s instructions).
- Replace worn parts as necessary.
Common Drone Problems and Solutions
| Problem | Cause | Solution | Prevention |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drone won’t take off | Low battery, faulty motor, or software glitch | Check battery, inspect motors, restart drone or update firmware | Regularly check battery levels, inspect components, and update firmware |
| Drone is unstable in flight | IMU or compass calibration issues, strong winds | Recalibrate IMU and compass, avoid flying in strong winds | Regular calibration, choose appropriate weather conditions |
| Poor camera quality | Dirty lens, incorrect settings | Clean the lens, adjust camera settings | Regular cleaning, understanding camera settings |
Proper Drone Storage
Store the drone in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Proper storage helps prevent damage and extends the drone’s lifespan. Keep the battery charged to around 50% storage capacity to prevent overcharging and prolong its lifespan. Consider using a desiccant pack to absorb moisture.
Drone Software and Apps
Drone software and apps are essential for controlling, configuring, and maintaining your drone. Understanding their features enhances the overall drone experience.
Drone Control Apps
Different drone manufacturers offer their own apps with varying features and interfaces. Some apps may offer advanced features like waypoint planning, autonomous flight modes, and camera control. Consider factors such as ease of use, available features, and compatibility with your drone model when choosing an app.
Firmware and Software Updates
Regularly updating your drone’s firmware and software is crucial for optimal performance and security. Updates often include bug fixes, performance improvements, and new features. Check for updates periodically through the manufacturer’s website or your drone’s app.
Drone Simulation Software

Drone simulation software allows you to practice flight skills in a safe and controlled virtual environment. This is particularly useful for beginners or for practicing advanced maneuvers without risking damage to your drone. Many simulators offer realistic flight physics and various environments to enhance the learning experience.
Mastering drone operation is a journey of learning and practice. By understanding the intricacies of drone components, implementing thorough pre-flight checks, and mastering both basic and advanced flight maneuvers, you’ll unlock the potential of aerial exploration and capture breathtaking perspectives. Remember to always prioritize safety and adhere to all regulations. Safe flying and happy soaring!
Popular Questions
What is the best drone for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones cater to beginners, often featuring simplified controls and safety features. Research models with good reviews and consider factors like flight time and camera quality.
Learning to operate a drone involves understanding its controls and safety protocols. A crucial step is familiarizing yourself with the various flight modes and functionalities. For comprehensive guidance on this, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone to enhance your skills and ensure safe operation. Ultimately, mastering how to operate a drone requires practice and adherence to regulations.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Calibrating your drone’s compass before each flight is recommended, especially if you’re flying in areas with strong magnetic interference. Consult your drone’s manual for specific instructions.
What should I do if I lose control of my drone?
If you lose control, immediately attempt to return the drone to its home point (if equipped). If unsuccessful, prioritize safety and contact local authorities if needed. Review your emergency procedures.
How do I register my drone?
Drone registration requirements vary by country and region. Check with your local aviation authority for specific regulations and registration processes.
